BETTER TOUCH BETTER BUSINESS
Contact Sales at Lori.
Generally speaking, CPU air coolers are divided into tower-type and downward-blowing types. If paired with ATX or M-ATX cases, most of the time, tower coolers are used. However, for ITX cases or some smaller M-ATX cases due to height constraints, downward-blowing coolers are required. Today, we'll discuss downward-blowing CPU air coolers, hoping to help everyone.
What is a Downward-Blowing Cooler?
A downward-blowing CPU cooler is a type of CPU cooler that dissipates heat through downward pressure. It typically consists of a metal plate (usually aluminum or copper) and a fan. The metal plate absorbs heat produced by the CPU during operation, and the fan transfers this heat into the air. The advantage of downward-blowing CPU coolers is their effective cooling of the CPU, ensuring it operates normally.
Differences Between Downward-Blowing and Tower Coolers
Downward-blowing CPU coolers are flat and placed directly on top of the processor, transferring heat to the heatsink through weight. In contrast, tower-type CPU coolers are three-dimensional, featuring a tower-shaped heatsink that expels heat through a fan.
The main difference between downward-blowing and tower coolers is their size. Generally, tower coolers are much taller than downward-blowing coolers, as they expel heat through a side-blowing method. Tower coolers also have a more complex structure and craftsmanship.
In terms of cooling performance, tower coolers are slightly superior. However, tower coolers are bulky and large, making them unsuitable for many ITX cases where height restrictions are often within 60mm. Such cases cannot accommodate tower coolers.
Advantages of Downward-Blowing Coolers
1. Quiet Operation: Downward-blowing coolers operate quietly, not affecting regular use, and the fan is relatively silent.
2. Ease of Installation: Downward-blowing coolers are easier to install and remove. Simply using a screwdriver or even hands to pry off the connection parts and CPU contact area can suffice. Some models require screws for fixation but do not require assembling the fan and heatsink or dealing with airflow issues.
3. Aesthetic Appeal: The design of downward-blowing coolers typically features cylindrical or square shapes, which better suit various case designs.
Uses of Downward-Blowing Coolers
Downward-blowing coolers are commonly used in smaller cases, such as many ITX cases, which have strict height restrictions for air coolers. Downward-blowing coolers are generally no taller than 60mm, with some models even under 50mm, allowing for maximum compatibility with small cases. Although tower coolers might have slightly better performance, this is not absolute. High-performance downward-blowing coolers are also available that match tower coolers in cooling effectiveness, depending on the user's needs.
Recommended Downward-Blowing Coolers
1. High-Cost-Performance Downward-Blowing Coolers
For those using i3, i5, or Ryzen R3, R5 platforms, the following high-cost-performance downward-blowing coolers are suitable. These CPUs have relatively low heat output, and these coolers are usually sufficient.
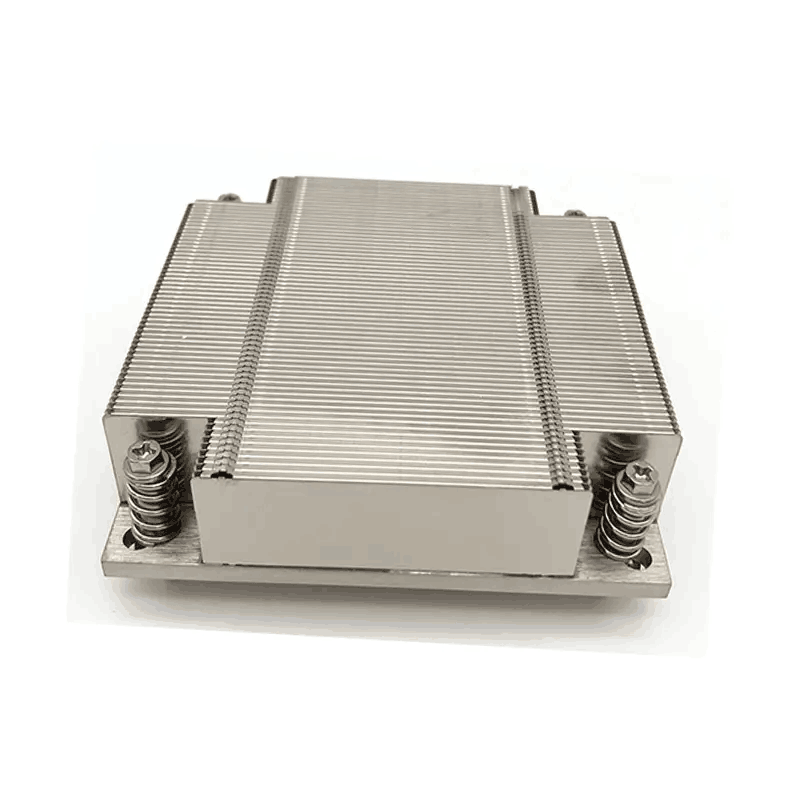
2. High-Performance Downward-Blowing Coolers
For high-performance users with i7 or higher platforms, which produce more heat, high-performance downward-blowing coolers are available that provide cooling performance comparable to tower coolers.
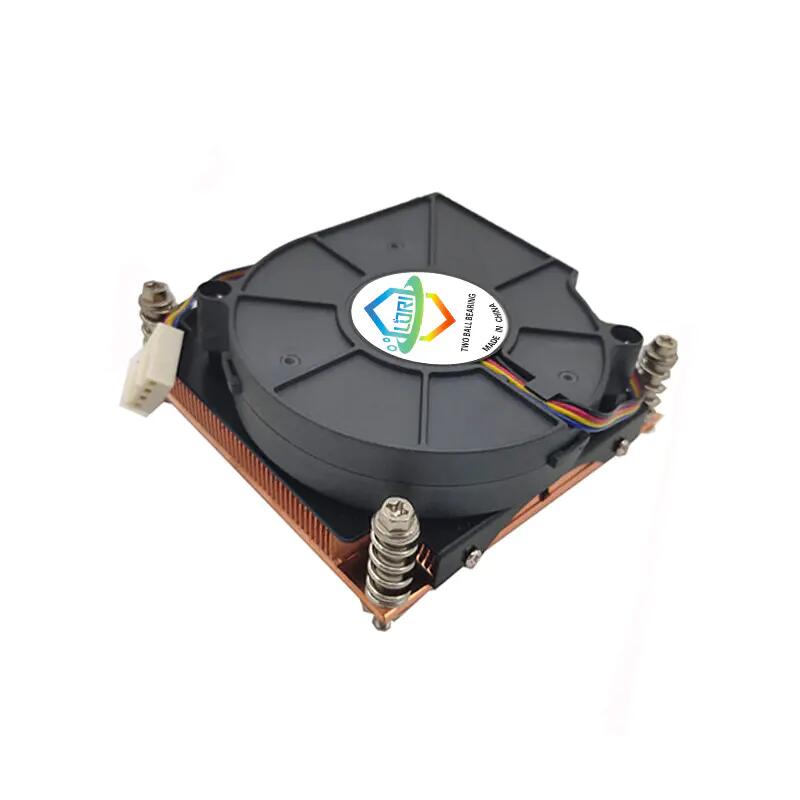
Copyright © 2025 Shenzhen Lori Technology Co.,Ltd. | All Rights Reserved